why do exogenous ketones cause diarrhea Ketones ketone acetone ketogenic bhb acetoacetate hydroxybutyrate urine metabolism breath salts hydroxybutyric powder ketosis perfectketo ketoacidosis fatty tissues nutritional exogenous
Starting on a new diet can be challenging, especially when you encounter unexpected challenges along the way. For those attempting a ketogenic diet, diarrhea may be one of those unexpected obstacles that they face. Did you know that diarrhea during keto can actually be quite common? Acetone, a byproduct of the body burning fat for fuel, can be the culprit. When you switch your body to a state of ketosis, you are essentially switching the body’s fuel source from glucose to fat. This process produces a byproduct called acetone, which can be excreted through sweat, breath, and urine. However, when the body produces too much acetone, it can lead to gastrointestinal discomfort such as diarrhea. While experiencing diarrhea during the adaptation period of a ketogenic diet is not unusual, it is still important to take steps to alleviate the symptoms. To start, make sure you are properly hydrating to offset any dehydration that may be caused by diarrhea. Additionally, increasing your intake of sodium and electrolytes can also help to reduce the severity of diarrhea symptoms. Another factor that can contribute to diarrhea on a ketogenic diet is the types of fats consumed. Some individuals may have a sensitivity to certain types of fats, causing gastrointestinal distress. For instance, medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) are frequently used as a supplement by those on a ketogenic diet. However, excessive MCT consumption can lead to diarrhea, as it can be difficult for the body to digest. If you are experiencing diarrhea on a ketogenic diet, it is essential to speak with your healthcare provider to determine the root cause of the issue. They may recommend adjusting your diet, increasing water and electrolyte intake, or slowing down the transition to a full ketogenic state. It is important to note that while diarrhea can be a common side effect of starting a ketogenic diet, it is not a necessary one. By properly hydrating, watching your fat intake, and seeking guidance as needed, you can mitigate these symptoms and focus on the many benefits of a ketogenic diet, such as weight loss and improved energy levels. In summary, diarrhea during a ketogenic diet can be a common occurrence due to the body producing excess acetone. To alleviate symptoms, it is essential to stay hydrated, increase electrolyte intake, and adjust your diet as necessary. And remember, if you continue to experience diarrhea, speaking with your healthcare provider is crucial to finding a solution that works for you.
If you are searching about Do Exogenous Ketones Break a Fast? | KetoaHolics you’ve visit to the right web. We have 5 Pictures about Do Exogenous Ketones Break a Fast? | KetoaHolics like Understanding the Ketogenic Diet: What is Acetone?, Do Exogenous Ketones Break a Fast? | KetoaHolics and also Understanding the Ketogenic Diet: What is Acetone?. Read more:
Do Exogenous Ketones Break A Fast? | KetoaHolics
 www.ketoaholics.comexogenous ketones ketoaholics minimize
www.ketoaholics.comexogenous ketones ketoaholics minimize
Understanding The Ketogenic Diet: What Is Acetone?
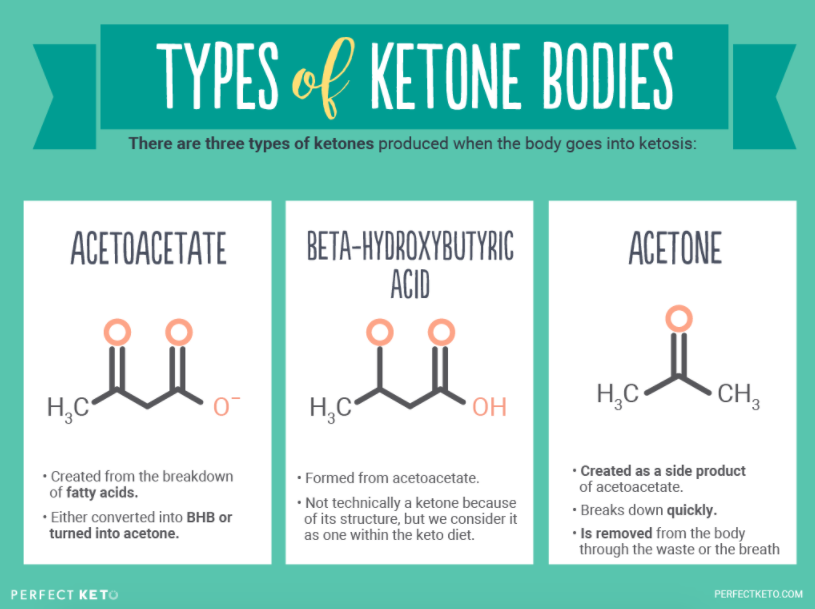 www.perfectketo.comketones ketone acetone ketogenic bhb acetoacetate hydroxybutyrate urine metabolism breath salts hydroxybutyric powder ketosis perfectketo ketoacidosis fatty tissues nutritional exogenous
www.perfectketo.comketones ketone acetone ketogenic bhb acetoacetate hydroxybutyrate urine metabolism breath salts hydroxybutyric powder ketosis perfectketo ketoacidosis fatty tissues nutritional exogenous
Keto Diarrhea Issues - Ketogenic Diarrhea During Keto Diet - Bee Healthy
 www.beehealthy.orgdiarrhea constipation ketogenic constipated risks everydayhealth successfully
www.beehealthy.orgdiarrhea constipation ketogenic constipated risks everydayhealth successfully
How To Use Exogenous Ketones For Weight Loss (2018 Guide) | BioKeto
 bioketo.comketones exogenous why bioketo naturally
bioketo.comketones exogenous why bioketo naturally
Why Exogenous Ketones Taste Bad - Perfect Keto
 perfectketo.comketones exogenous taste ketone perfectketo summarize dilute
perfectketo.comketones exogenous taste ketone perfectketo summarize dilute
Understanding the ketogenic diet: what is acetone?. Exogenous ketones ketoaholics minimize. Ketones ketone acetone ketogenic bhb acetoacetate hydroxybutyrate urine metabolism breath salts hydroxybutyric powder ketosis perfectketo ketoacidosis fatty tissues nutritional exogenous